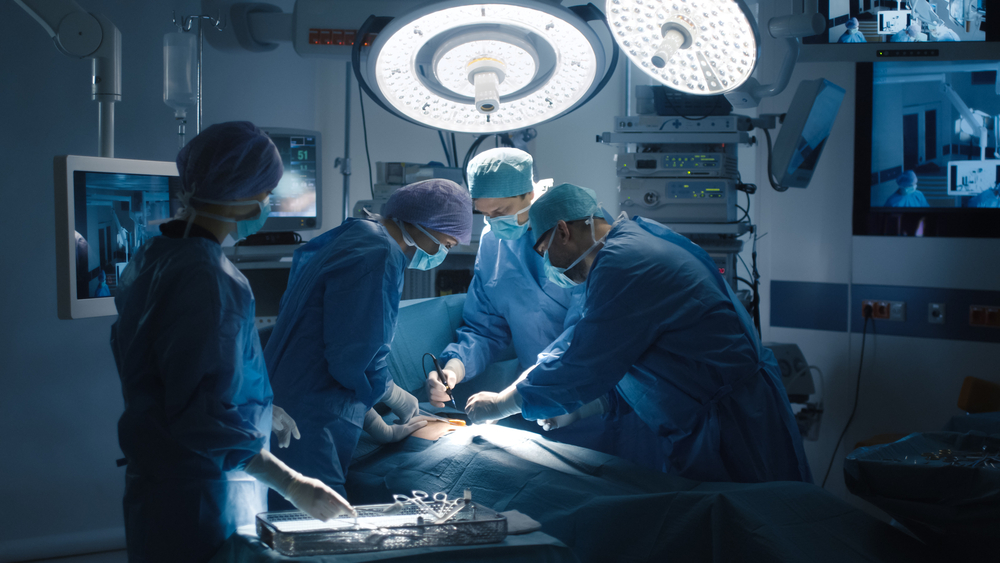

Key Gases and Guidelines for Keyhole Surgery
Gases are used to inflate all kinds of objects – party balloons, hot air balloons, blimps – but they are also an essential medical gas for inflating the body in order to perform endoscopic surgeries. Now, we aren’t only talking about Helium, but also gases like Carbon Dioxide and Nitrous Oxide. An endoscopy is a “key hole” surgery that uses an instrument called an endoscope to view – or scope out – the inside of the body. The tip of the endoscope has a tiny light and camera that streams onto a screen so that doctors can effectively see the body’s interior in the most minimally invasive way possible. Because there is only a small incision site, this outpatient procedure is praised for reduced pain during recovery, reduced scarring, improved cosmetic results.
There are many different types of endoscopic surgeries that target various areas of the anatomy to diagnose diseases, screen for cancer, perform biopsies, and give treatment. What once was only used for treating the stomach, colon and esophagus is now also used for some of the following procedures:
– Arthroscopy: joints
– Bronchoscopy: trachea and bronchi of the lungs
– Colonoscopy: colon
– Cystoscopy: inside of the bladder
– Laparoscopy: stomach, liver, and other abdominal organs
– Laryngoscopy: larynx
– Neuroendoscopy: brain
A key part of this key hole surgical technique is an insufflation gas, which inflates the interior of the body by enlarging the area so that doctors have increased visibility of the surgical area. This is especially essential in laparoscopic surgeries, where the organs (stomach, large, small intestines, kidneys, liver, etc.) are in close proximity to one another. The most widely used medical gas for insufflation is medical Carbon Dioxide, which is easily soluble in the blood stream. A cannula inflates the abdomen or other surgical areas via one of the one to four incision sites with a constant stream of CO2 at a pressure of 15 mm Hg. The pressure should never exceed 25 mm Hg, or else there are more evident health risks.
The Preferred Insufflation Gas
Why is CO2 used more commonly than Helium or Nitrous Oxide? Well, CO2 is the preferred medical gas for endoscopies because it is colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and it is highly soluble in the blood stream and therefore easily removed by the body. However, depending on patient health history, Helium or Nitrous Oxide may be a better option. For example, patients who have any types of cardiac disease can experience cardiac arrhythmias when CO2 is used, making Nitrous Oxide a safer alternative. Yet, CO2 has the lowest risk of gas embolism and is one of the cheaper medical gases on the market.
Updated FDA Requirements for Medical Gases
The FDA updated their draft on “Current Good Manufacturing Practice for Medical Gases Guidance for Industry” for the first time in 2017 since 2003. The comprehensive draft includes the requirements for production and process controls, packaging and labeling controls, and sampling and testing.
The draft is targeted toward manufacturers to ensure best practices that will provide hospitals with the highest purity and safely manufactured gases on the market. These requirements include thorough records that identify the identity and quantity of each shipment, include the supplier’s name, lot number, date of receipt, and documentation of any test results and examinations. It states that “testing alone cannot ensure product quality.” The proper testing, authorization, and certification must be implemented for medical gases to have high enough quality to be delivered to the customer. The entire text can be read here.
An FDA Compliant Medical Gas Distributor
Rocky Mountain Air is compliant with the FDA guidelines for current good manufacturing practices, ensuring that the medical gases purchased from us have been manufactured, processed, and packed according to the requirements and include the proper documentation. With our dedication to flawless dependability, we work hard to provide medical gases that are of high purity and are safe to use for your medical applications such as CO2 for insufflation in endoscopic surgeries. Our PurityPlus specialty gases receive certifications of purity upon being tested that are provided with each cylinder.
Whether you are a current or prospective customer, if you have any questions about our high purity medical gases, please contact your local branch in any one of our five states (Colorado, Utah, Idaho, Wyoming, Nebraska) today. We look forward to serving you.